Retrieval Augmented Generation(RAG)
.png)
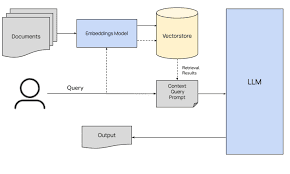
We Know core ideas like NLP, LLM. Let's look at how we might build utilizing LLM and the deployment aspect using RAG. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a technique in natural language processing that combines retrieval-based and generation-based approaches to create more accurate and informative responses. Let's break down each point: 1. RAG Architecture Architecture: Retriever: Retrieves relevant documents or passages from a large corpus based on the input query. Reader/Generator: Uses the retrieved documents to generate a coherent and relevant response. Combiner: Integrates the retrieved information with the generated response. 2. Pipeline Behind the RAG The RAG pipeline is a collection of the above components working together: Query Processing: The input query is encoded into a vector. Retrieval: The encoded query is used to retrieve relevant documents from a vector database. Document Encoding: The retrieved documents are encoded into vectors. Information Inte...


